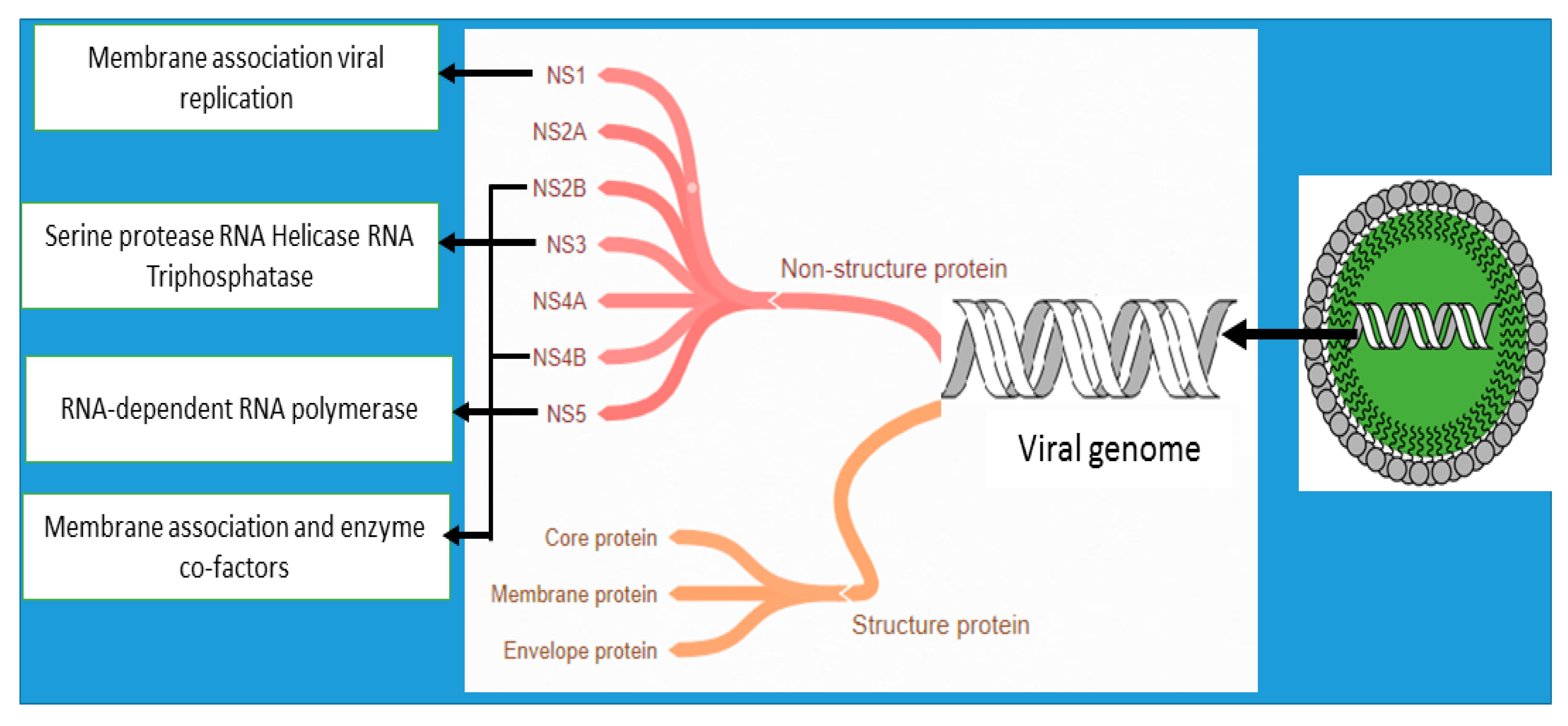
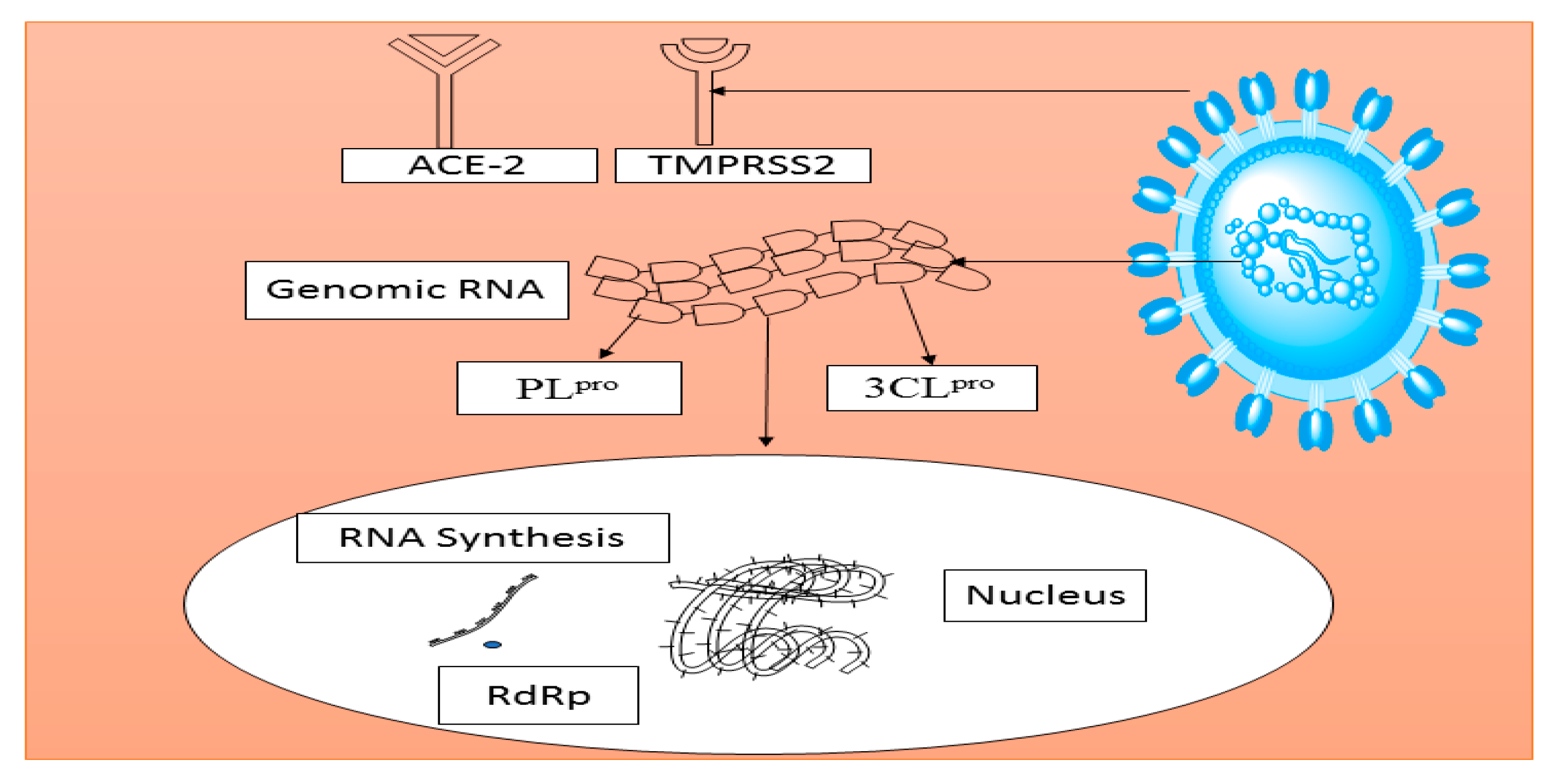
Transgenic Plants And Animals Wikipedia

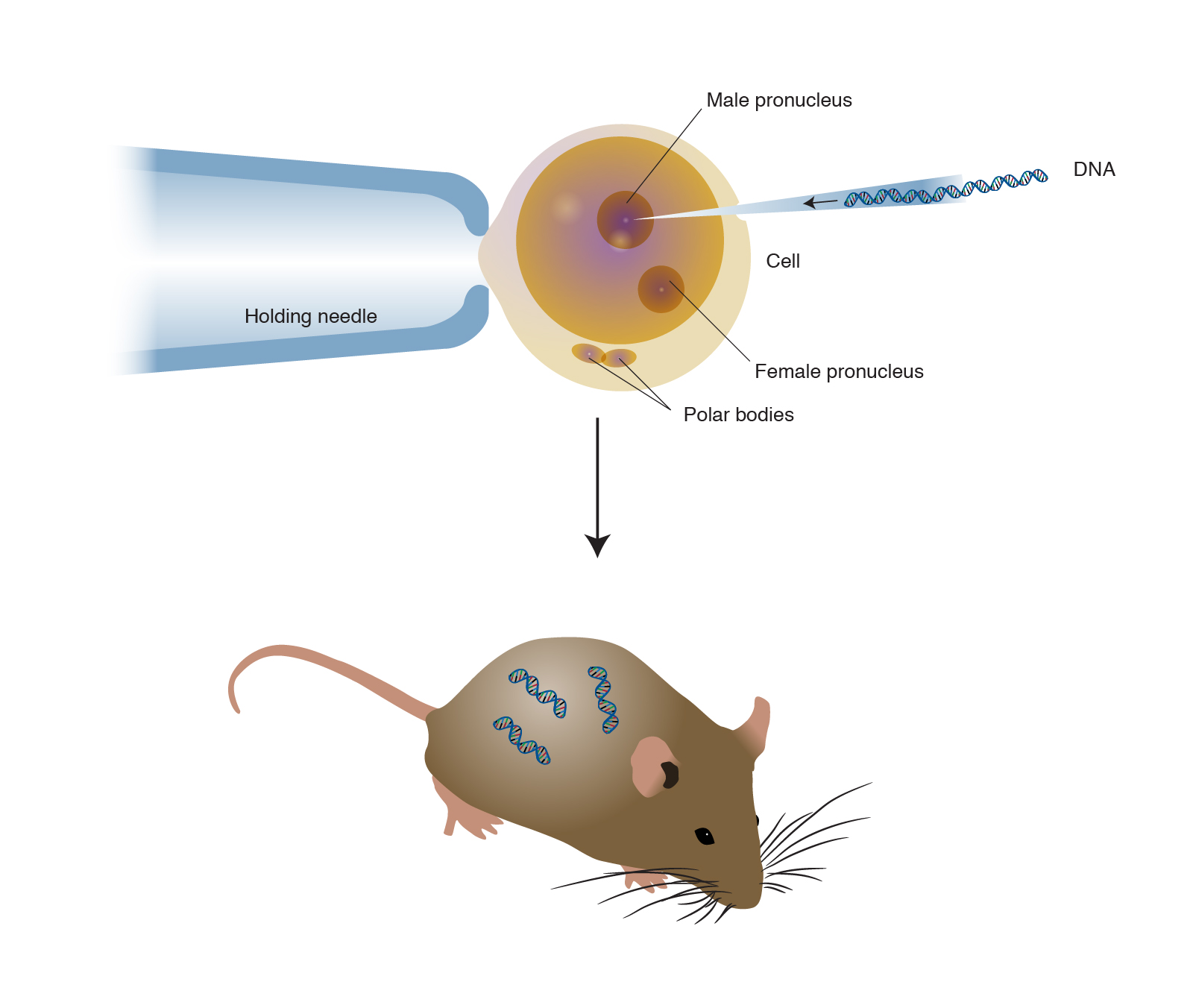
Following natural gestation and birth offspring are subject to tissue biopsy and blood sampling.
Transgenic plants and animals wikipedia. A transgenic animal is one that carries a foreign gene that has been deliberately inserted into its genome. Usually ear tissue and blood are screened by polymerase chain reaction andor Southern analysis for the. By the year 1998-99 five major transgenic crops cotton maize soybean canola and potato were in widespread use.
Transgenic Plants as Bioreactor Molecular Farming. It was in 1995-96. Transgenic animals for the production of therapeutic and diagnostic proteins are produced by transferring fertilized transgene-carrying embryos to recipient animals.
A foreign gene will be inserted into a plant of a different species or kingdom. Transgenic plants potato and cotton were for the first time made available to farmers in USA. Plant can be used as bioreactor transgenic plants which can be used to produce the proteins or peptides encoded by the introduced foreign genes in vaccine production against animal and human diseases.
Transgenic plants are plants that have had their genomes modified through genetic engineering techniques either by the addition of a foreign gene or removal of a certain detrimental gene. For this reason the desired genes are cloned and expressed in animals such as sheep goats chickens and mice. Transgenic plants are plants that have been genetically engineered a breeding approach that uses recombinant DNA techniques to create plants with new characteristicsThey are identified as a.
Applications of animal transgenesis may be divided into three major categories. Animal life is possible due to plants. The foreign gene is constructed using recombinant DNA methodology.
The monoclonal antibodies peptide hormones cytokinins and blood plasma proteins are being produced in transgenic plants and their parts such as tobacco in leaves potato in tubers sugarcane in stems and maize in. A transgenic animal is one that carries a foreign gene that has been inserted into its genome. Transgenic models are more precise in comparison to traditional animal models for example the oncomouse with its increased susceptibility to tumor development enables results for carcinogenicity studies to be obtained within a shorter time-frame thus reducing the course of tumor development in experimentally affected animals.