Cellular Respiration Meaning In Biology

Metabolism refers to a set of chemical reactions carried out for maintaining the living state of the cells in an organism.
Cellular respiration meaning in biology. Cellular respiration the process by which organisms combine oxygen with foodstuff molecules diverting the chemical energy in these substances into life-sustaining activities and discarding as waste products carbon dioxide and water. Signal transduction The transmission of signals from a cells outside to its inside. Cellular respiration biology definition.
To create ATP and other forms of energy to power cellular reactions cells require fuel and an electron acceptor which drives the chemical process of turning energy into a useable form. Google Classroom Facebook Twitter. Introduction to Cellular Respiration.
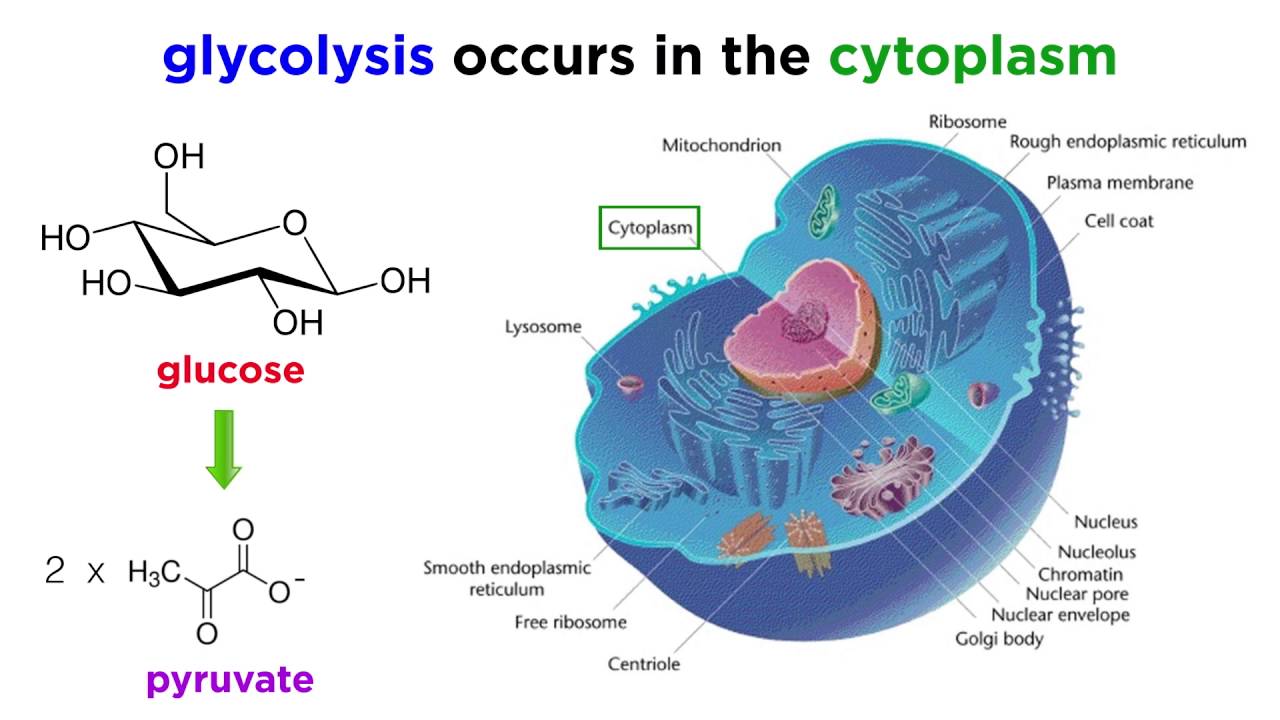
Cellular respiration is a set of metabolic reactions and processes that take place in the cells of organisms to convert chemical energy from oxygen molecules or nutrients into adenosine triphosphate ATP and then release waste products. The process takes place in the cytoplasm of a cell. During cellular respiration glucose in the presence of oxygen is converted into carbon dioxide and water.
The process of cell catabolism in which cells turn food into usable energy in the form of ATP. In the cells of any non-photosynthetic eukaryote such as a person bread mold or a paramecium glucose and oxygen are going to come from outside the cell. A series of metabolic processes that take place within a cell in which the biochemical energy is harvested from an organic substance eg.
Based on the oxygen demand cellular respiration is divided into- Aerobic respiration and Anaerobic respiration. The cellular context In the diagram at left 1 represents the cell exterior. Aerobic respiration requires oxygen to fully oxidise the organic molecule.
Other types of organisms such as animals fungi many protozoa and a large. Cellular respiration is a biological process in which cells convert sugar amino acids and fatty acids into energy utilized by the cell. In this process glucose breaks down without the help of oxygen and the by-products produced are alcohol CO2 and energy or ATP.