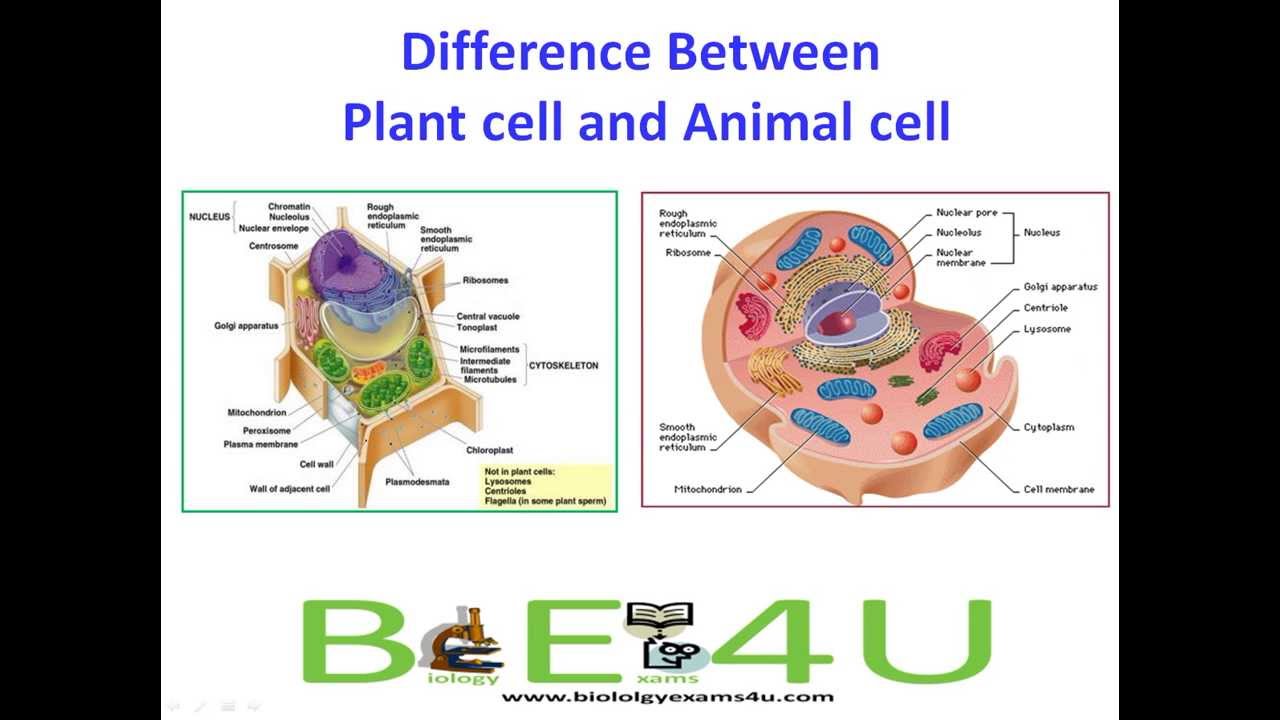
Plants And Animals Cells
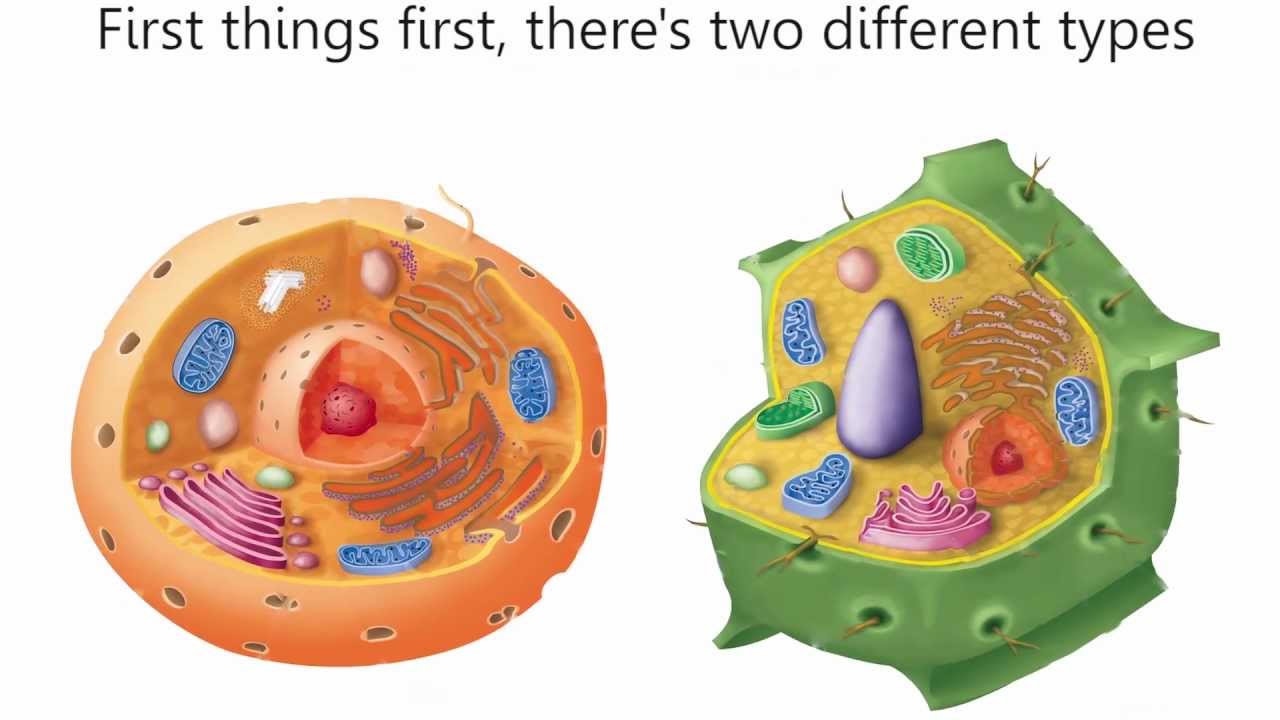
The plant cell can also be.
Plants and animals cells. In both animals and plants cells generally become specialized to perform certain functions. Despite many similarities plant and animal cells differ in a few different ways. Nerve cells bone cells and liver cells for example all develop in ways that enable them to better perform.
Plant cells are generally larger than animal cells as animal cells can be around 10-30 micrometers while plant cells can range from 10-100 micrometers. Both plant and animal cells comprise membrane-bound organelles such as endoplasmic reticulum mitochondria the nucleus Golgi apparatus peroxisomes lysosomes. Beyond the cell walls major differences between the two are the existence of chloroplast vacuoles and a cell wall within plant cells.
Plant cells are autrotrophs meaning they are able to make their own food while animal cells are heterotrophs meaning they have to take in nutrition from outside sources such as plants or animals. The clear differences are the lack of cell walls chloroplasts and vacuoles and the presence of flagella lysosomes and centrosomes in animal cells. Label a plant and animal cell.
Differences between plant fungal and animal cells. Even though plant and animal cells are eukaryotic and share a few cell organelles plant cells are quite distinct when compared to animal cells as they perform different functions. PLANT AND ANIMAL CELLPLANT AND ANIMAL CELLS SSS Organelle Function Cell Membrane A double layer that supports and protects the cell.
Lysosome Contains digestive enzymes that destroy damaged organelles and invaders. Plant and fungal cells have cell. They also have similar membranes such as cytoskeletal elements and cytosol.
The plant cell is rectangular and comparatively larger than the animal cell. Some of the major organelles include the nucleus mitochondria lysosomes the endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi apparatus. Plant and Animal Cells.