Cell Membrane Structure And Function A Level

In plant cells the membrane encapsulates the protoplasm.
Cell membrane structure and function a level. The plasma membrane is impermeable to ions and most water-soluble molecules. Images obtained through electron micrography reveal the bilayer structure of cell membranes. Cell membrane is a protective covering that acts as a barrier between the inner and outer environment of a cell in animals.
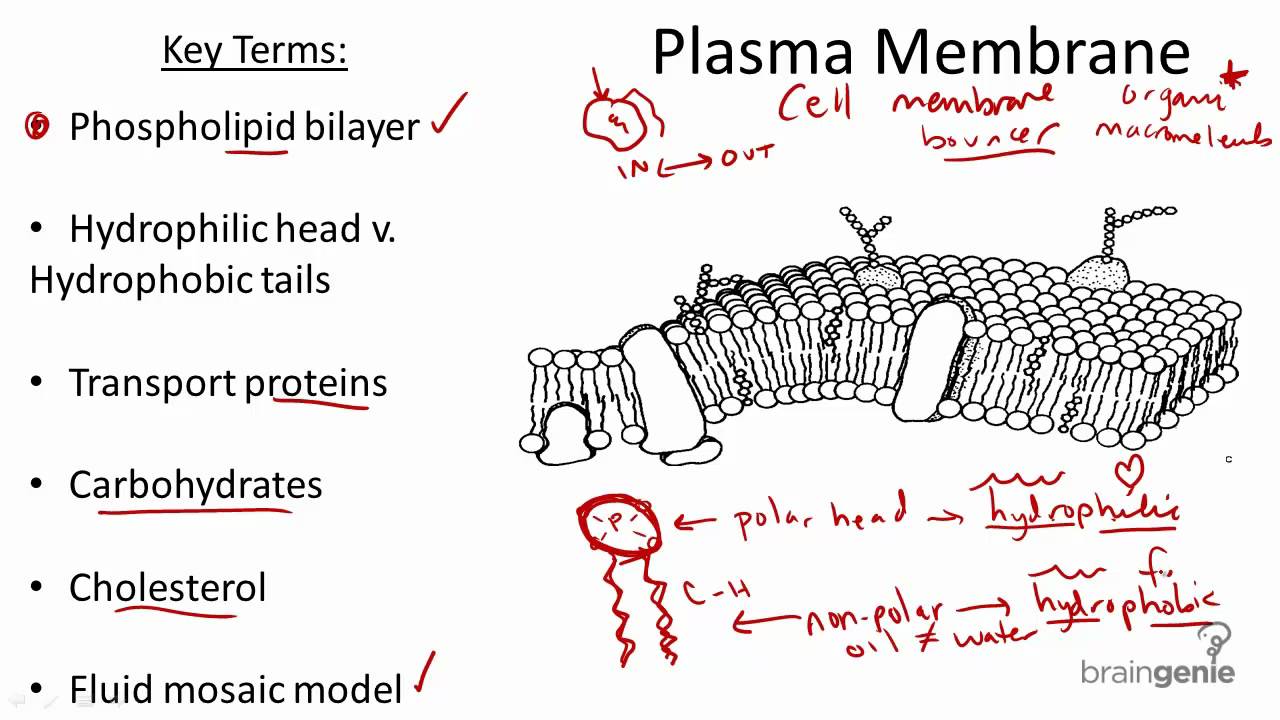
Functions of membrane systems and organelles. Because the membrane is fluid and because of the mosaic arrangement of the protein molecules the structure of the membrane. The fundamental structure of the plasma membrane.
Membranes are selectively permeable so are effective barriers in controlling what goes in and out of cells. The Nucleus is the largest organelle in a cell. The fine detail of the cell which may be revealed by an electron microscope is called the cells ultrastructure.
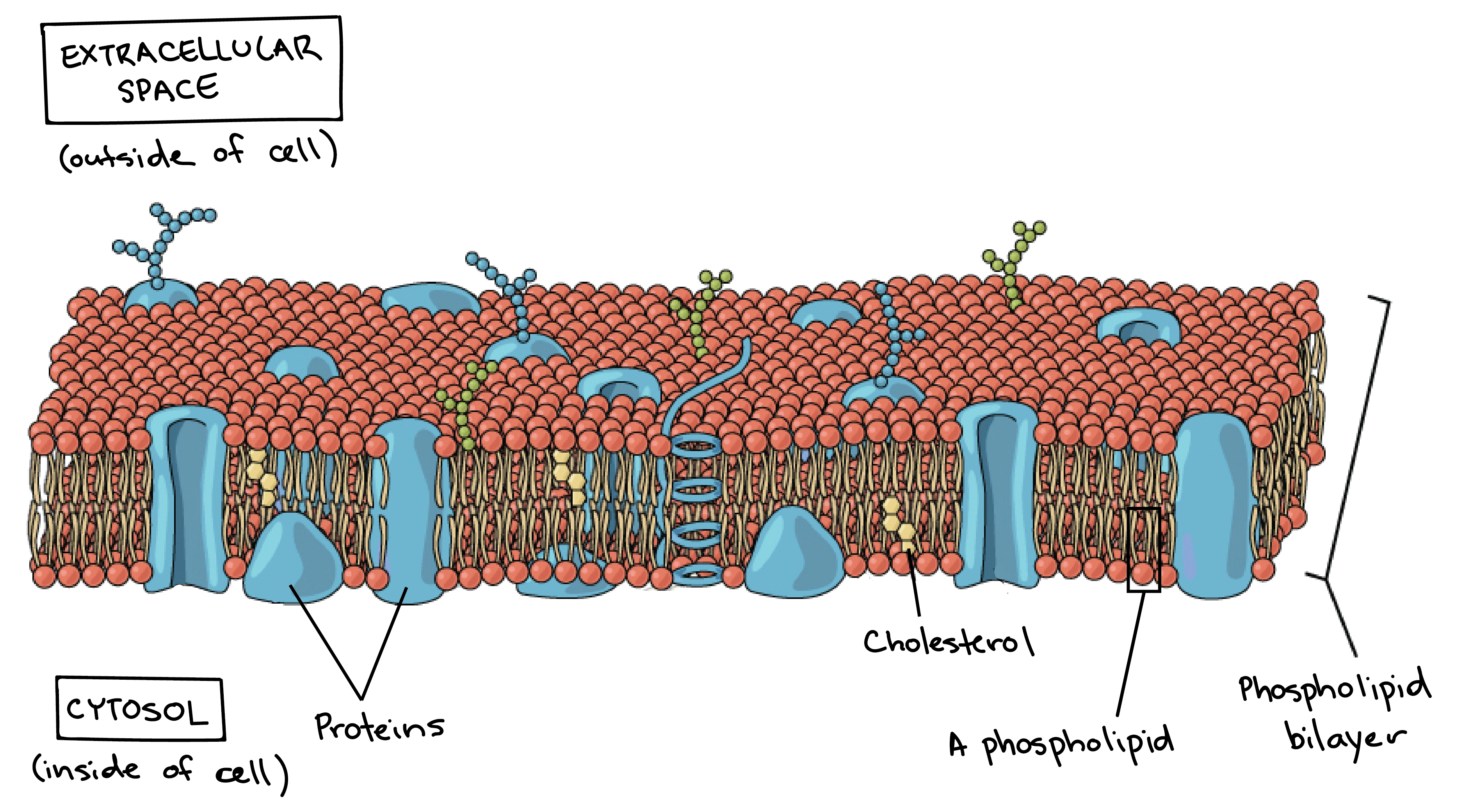
This structure can even be called the inner membrane to distinguish it from the outer membrane present in gram-negative bacteria. Membranes formed from phospholipid bilayers help to compartmentalise different regions within the cell as well as forming the cell surface membrane Exam Tip An example of a membrane-bound organelle is the lysosome found in animal cells each containing many hydrolytic enzymes that can break down many different kinds of biomolecule. The nucleus is surrounded by nuclear envelope pair of membranes.
The liquid where all. Contains chromosomes DNA code for the synthesis of proteins that control the function of the cell hence the nucleus commands the cell Cell Surface membrane. Some of these proteins span the whole width of the membrane.
The Formation of Cell Membranes is Crucial to Life. The membrane also contains membrane proteins including integral proteins that go across the membrane serving as membrane. Animal Cell Structure Nucleus.